6.1 The WuKong Profile Framework (WKPF)
Before we show how to implement a WuClass, we give a brief introduction on how a WuKong device runs the application using WuClasses. This presentation is helpful for understanding the WuClass implementation.
The following figure shows a view on the software structure of a WuKong node. The most important module is the Profile Framework (WKPF) which manages the WuKong classes and objects running on the node. The node also keeps a Link Table which is created by WuKong Master to specify where a new local property value should be propagated to a remote node. Finally, a node may have many WuObjects, each with an update function running periodically (based on individual refresh rates) or running responsively (based on property propagation). Each WuObject runs the code defined by its WuClass, including the property types and the update method.
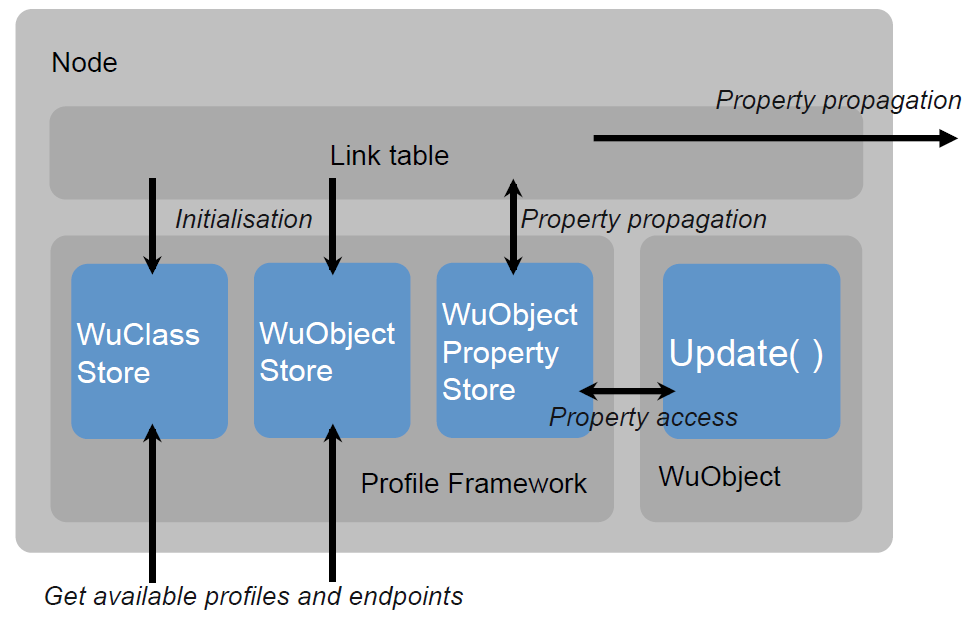
Profile Framework
The WuKong Profile Framework (WKPF) is an application framework for WuKong devices. While an FBP defines the logical view of the application, WKPF tracks the physical resources on the networks and manages the communication between them.
The framework has four main responsibilities:
- Load WuClasses and create new WuObject instances on a node.
- Allow Master to discover which WuClasses and WuObjects are available on a node.
- Trigger executions within WuObjects, either periodically or as a result of changing data (from sensing hardware or network).
- Propagate changes between linked properties of WuObjects, which may be hosted locally, or on a remote node.
Property
Property is the basic data unit of WKPF. Properties of an WuClass are the primary way to control an Wuobject. As we will see the definition of WuClass in the next section, each property has four attributes including name, access, datatype and default value.
WuClass and WuObject
As its name, WuClass is a class similar to the class in the object oriented programming. It is used to define a set of data and methods in order to create some "objects" for the wukong. Those objects are called WuObject in wukong. WuObjects are the main units of processing in an application and are hosted on the nodes.
WuObject Property Store
The properties of an WuObject are managed by the profile framework in a common property store. The framework provides functions for an WuObject to access its data within the update() method. This allows the framework to monitor the changes that an object makes to its properties, and to propagate them to connected destination WuObjects if necessary.
Update Method
update() method is a function which implements the class’ behaviour. The function will be called whenever a property changes value, or periodically according to the refresh rate schedule. Once be called, WuObject will respond to a change in one of its inputs according to the behaviour defined in the update method. Therefore, writing a wuclass is all about writing update method.
An important point to remember is that an WuObject does not store its properties by itself. The properties are stored by WKPF which is responsible for monitoring and propagating changes. Therefore, an WuObject has to communicate with WKPF to read and update its properties.
Basically each update function has three phases:
- read input properties from the profile framework
- do some processing
- write output properties to the profile framework
For example, a simple sensor like a button skips the first step and just do the processing (take a measurement) and write the result to its output property. An actuator like a light actuator does not have any output, so it skips the third step and only reads its input and turns the light on or off accordingly.
Link Table
This table stores the source property and the destination property of every link on an FBP. The node will obtain this table after deployment.
The LED Control FBP Example
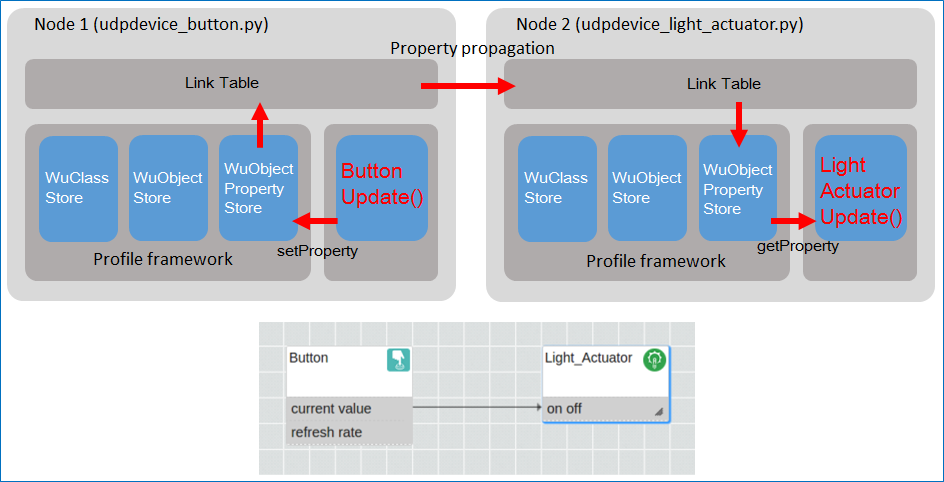
To explore the LED control FBP of Section 4.2, we will go through the steps from "add node" to "testing", and see how those steps relate to the above diagram.
Add node
When we add a node to WuKong as in Section 4.2.2, the node will be initialized. That is, WuClasses are loaded and new WuObject instances are created on a node.Discovery
When we press "Discover node" button, Master will collect the information of WuClasses and WuObjects on every node.Map
According to the information of WuClasses and WuObjects, Master will map all FBP components to the WuObjects of some nodes.Deploy When we press "Deploy" button, a node will get a link table from Master so that it will propagate its value according to the link table. The profile framework will also get available profiles and endpoints on the field from master.
Testing
After we press the physical button, the periodic update method of button WuObject will transmit data to the WuObject property store. And next, the profile framework will propagate changes between linked properties of the WuObjects, which may be hosted locally, or on a remote node.Finally, the light actuator WuObject will be triggered by the profile framework and get the data from the WuObject property store. Therefore, the light will be turned on or off accordingly.
Function to access property from the update() method
The functions which will be used to access property in the next section are:
def setProperty(self,pID,val):
self.cls.setProperty(self.port,pID,val)
def getProperty(self,pID):
return self.cls.getProperty(self.port,pID)
setProperty will write output properties to the profile framework.
getPropert will read input properties from the profile framework.
These are two methods of the WuObject defined in the